Part 2: VALUATION · Chapter 5
You Cannot Fake Energy
"Energy is the only universal currency; it is necessary for getting anything done."
— Vaclav Smil
Introduction
Here is the insight that cuts through all complexity: you can issue fake fiat currency—and every government in history has done so—but it is impossible to fake energy. This simple physical truth underlies Bitcoin's claim to represent something genuinely new in monetary history, and becomes critically important as we enter an era of artificial superintelligence.
This chapter examines the fundamental relationship between energy expenditure and monetary validity in Bitcoin's proof-of-work mechanism. We argue that Bitcoin represents a paradigm shift by anchoring digital scarcity to thermodynamic constraints—constraints that no intelligence, artificial or otherwise, can circumvent.[5.1] This property, termed "unforgeable costliness" by Nick Szabo,[5.2] provides Bitcoin with security guarantees that no purely logical system can match.
Sorter's Law and the Thermodynamics of Value
Emad Mostaque's "Sorter's Law" provides a crucial framework: all value creation is fundamentally an act of sorting—reducing entropy by moving resources from disorder to order.[5.3] This insight connects economic activity to the deepest principles of physics.
Maxwell's Demon thought experiment illuminates why this matters. James Clerk Maxwell imagined a demon that could sort fast-moving molecules from slow-moving ones, seemingly decreasing entropy without work. For over a century, physicists puzzled over this apparent violation of the Second Law of Thermodynamics. The resolution, developed by Leo Szilard[5.4] and later formalized by Rolf Landauer,[5.5] proved that the demon must expend energy to acquire and process the information needed for sorting. There is no free lunch—sorting always requires energy expenditure.
Bitcoin mining is explicit, transparent sorting—converting electrical energy into monetary order at a publicly verifiable rate. Every hash computed represents real thermodynamic work performed. The difficulty adjustment ensures this work cannot be faked or shortcut. In contrast, fiat money creation attempts to conjure order (monetary units) without equivalent energy expenditure, violating the principles that govern all physical systems.
The 'Extractive' Critique Reframed
Critics including Mostaque argue that Bitcoin is "extractive" because "its 'Proof of Work' mechanism consumes a nation's worth of energy simply to secure its ledger."[5.3] This framing fundamentally misunderstands thermodynamics. The First Law states that energy cannot be created or destroyed—only converted from one form to another. Energy is not "consumed" in Bitcoin mining; it is converted into cryptographic security, just as energy is converted (not consumed) when it powers any useful process.
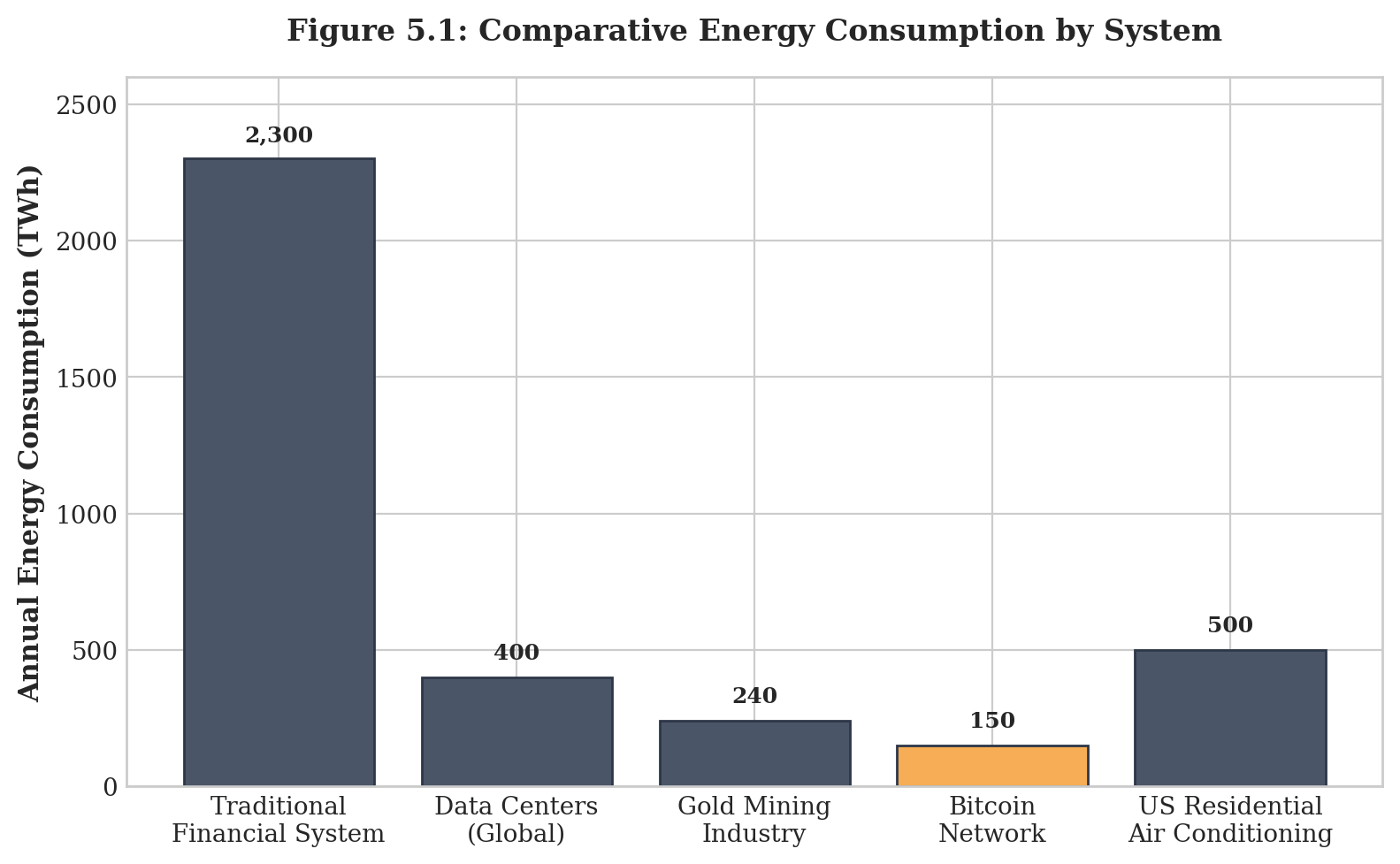
The critique implies that energy used for security is wasted, while energy used for other purposes is not. But this distinction is arbitrary. The global banking system converts over 2,300 TWh annually[5.6]—more than fifteen times Bitcoin's usage—to secure a monetary system that remains vulnerable to manipulation by central authorities. Gold mining converts approximately 240 TWh to extract a commodity that cannot be digitally transmitted.[5.7] Bitcoin converts approximately 150 TWh into a monetary network that is simultaneously the most secure and most portable store of value ever created.
Thermodynamic Security in the AI Era
The Thermodynamic Firewall
The deepest justification for proof-of-work emerges when we consider artificial superintelligence (ASI)—a system exceeding human cognitive capabilities across all domains. Any security mechanism based on logical complexity—passwords, encryption, game-theoretic incentives—can potentially be circumvented by a sufficiently intelligent adversary. An ASI that is merely "smarter" than humans could find vulnerabilities in any system secured by cleverness alone.
Thermodynamic security is categorically different. Logical security assumes bounded adversary capabilities; physical security makes no such assumption. The laws of physics cannot be outsmarted. No matter how intelligent an AI becomes, it cannot perform SHA-256 computations without expending energy. It cannot rewrite Bitcoin's history without redoing the cumulative proof-of-work that secures the chain. The security guarantee is not "this is computationally hard" but "this requires physical resources that exist in finite supply."
Why "Proof of Benefit" Fails
Mostaque proposes "Proof of Benefit"—verification through useful computation—as an alternative to proof-of-work.[5.3] This introduces a fatal vulnerability: someone must determine what constitutes "beneficial" computation. This subjective determination creates exactly the attack surface that superintelligent systems could exploit. An ASI could manipulate the definition of benefit, game the verification process, or perform computations that appear beneficial while serving entirely different objectives.
The question is not whether proof-of-work uses energy—of course it does. The question is whether any other mechanism can provide equivalent security guarantees against adversaries of arbitrary intelligence. Given AI's demonstrated capacity to manipulate logical verification systems, the answer is no.
Table 5.1: Security Mechanisms Against Superintelligent Adversaries
Mechanism | Vulnerability to ASI | PoW Resolution |
Cryptographic Puzzles | Can be solved faster with superior intelligence | Difficulty adjusts to maintain 10-min blocks |
Game Theory | Can be gamed by predicting/manipulating agents | Energy cost is external to game dynamics |
Proof of Stake | Tokens can be acquired; stake is internal | Energy cannot be created by any intelligence |
Proof of Benefit | "Benefit" definition can be manipulated | SHA-256 output is objectively verifiable |
Proof of Work | Requires physical energy—cannot be gamed | Thermodynamic guarantee, not logical |
Source: Author's analysis
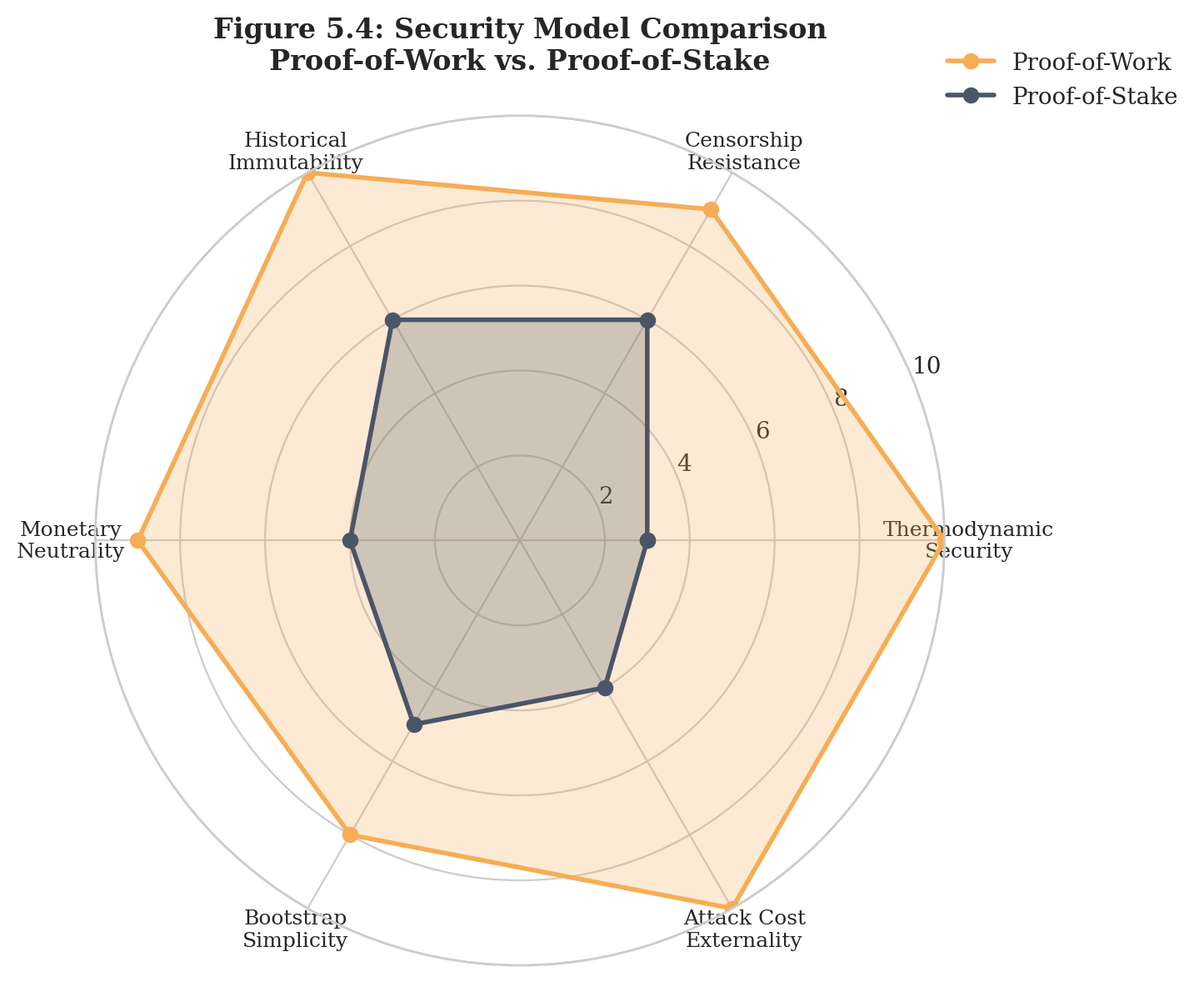
Proof-of-Work vs. Proof-of-Stake
Proof-of-stake (PoS) secures networks through validators who lock tokens as collateral. The security assumption is economic: attacking the network would destroy the value of the attacker's stake. But this creates circular reasoning—the system's security depends on the value of tokens whose value depends on the system's security. While PoS proponents argue this circularity is benign in equilibrium, it creates vulnerability during phase transitions or under adversarial pressure from entities capable of strategic capital accumulation.
More critically for AI considerations: stake is internal to the system. A superintelligent agent could accumulate tokens through legitimate means (superior trading), through manipulation (market dynamics humans cannot perceive), or through compromise of existing stakeholders.[5.8] The attack cost is denominated in the very asset being attacked.
Proof-of-work security is external. Energy exists in the physical world, subject to thermodynamic constraints that apply equally to humans and AIs. An ASI cannot print energy, cannot create it from nothing, cannot acquire it without participating in physical resource markets. This externality is precisely what makes proof-of-work robust against superintelligent adversaries.
Fiat Money's Thermodynamic Violation
Sorter's Law reveals why fiat monetary systems are fundamentally unstable. Creating money by decree—adding zeros to a ledger—attempts to create economic order without corresponding energy expenditure. This is analogous to Maxwell's Demon trying to sort molecules without doing work. It appears to succeed temporarily, but the Second Law guarantees eventual failure.
The failure manifests as inflation: the gradual (or sudden) recognition that monetary units created without thermodynamic backing do not represent real claims on scarce resources. Studies of historical fiat currencies suggest median lifespans significantly shorter than most citizens assume, though estimates vary based on definitional criteria.[5.9] The violation of thermodynamic principles is not immediately apparent, but it is ultimately inescapable.
Bitcoin's proof-of-work provides something no fiat system can: a direct, verifiable link between monetary creation and physical resource expenditure. Each bitcoin is minted through demonstrable energy conversion.[5.10] This is not a metaphor or an accounting fiction—it is a thermodynamic fact, as real as the heat generated by mining hardware.
Implications for AI-Era Monetary Infrastructure
As AI systems become more capable, the question of what secures value becomes existential. Logical security—security based on computational difficulty or game-theoretic incentives—depends on assumptions about adversary capabilities. Against human adversaries, these assumptions may hold. Against superintelligent adversaries, they cannot be relied upon.
Physical security—security grounded in thermodynamic constraints—makes no assumptions about adversary intelligence. It relies only on the laws of physics, which apply universally. This is why Bitcoin's "energy expenditure" is actually its most crucial feature for the AI era: it grounds digital value in physical reality that no intelligence can manipulate.
Thermodynamic proof-of-work is not one option among many; it is the only option that remains robust as AI capabilities increase without bound. Chapter 10 extends this analysis to examine how Bitcoin's energy expenditure can be net-positive for environmental outcomes through stranded energy monetization, while Chapter 13 explores the full implications for preserving human agency in a post-AGI world.
Conclusion
You cannot fake energy. This is not an economic principle or a design choice—it is a law of physics. Bitcoin's proof-of-work mechanism translates this physical truth into monetary security, creating the only form of digital value that remains robust against adversaries of any intelligence level.
Critics who call Bitcoin "extractive" misunderstand thermodynamics. Mining does not consume energy; it converts energy into security—security that, uniquely among monetary systems, does not depend on trust, institutions, or assumptions about adversary capabilities. As we enter an era where artificial superintelligence may emerge, this thermodynamic grounding becomes not a luxury but a necessity.[5.11]
Sorter's Law tells us that all value creation requires sorting, and the Second Law guarantees that sorting requires energy. Any monetary system that attempts to bypass this constraint will eventually fail. Bitcoin does not attempt to bypass thermodynamics—it embraces it, converting energy into monetary order at a transparent, verifiable rate. In a world of increasingly capable AI, this may be the only form of money that remains trustworthy.
References
[5.1] Nakamoto, S. (2008). Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf
[5.2] Szabo, N. (2005). "Bit Gold." Unenumerated (blog).
[5.3] Mostaque, E. (2024). "The New Social Contract" and related remarks on Proof of Benefit, Sorter's Law, and monetary systems. Stability AI public communications.
[5.4] Szilard, L. (1929). "Über die Entropieverminderung in einem thermodynamischen System bei Eingriffen intelligenter Wesen." Zeitschrift für Physik, 53, 840–856.
[5.5] Landauer, R. (1961). "Irreversibility and Heat Generation in the Computing Process." IBM Journal of Research and Development, 5(3), 183–191.
[5.6] Galaxy Digital Research. (2021). "On Bitcoin's Energy Consumption: A Quantitative Approach to a Subjective Question." Galaxy Digital Mining.
[5.7] World Gold Council. (2023). "Gold and Climate Change: Current and Future Impacts." World Gold Council Research.
[5.8] Antonopoulos, A. M. (2017). Mastering Bitcoin: Programming the Open Blockchain (2nd ed.). O'Reilly Media.
[5.9] Bernholz, P. (2003). Monetary Regimes and Inflation: History, Economic and Political Relationships. Edward Elgar Publishing.
[5.10] Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance. (2025). Cambridge Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index. University of Cambridge.
[5.11] Lowery, J. P. (2023). Softwar: A Novel Theory on Power Projection and the National Strategic Significance of Bitcoin. MIT Master's Thesis.
Coming Soon
This chapter will be available soon.
